2022-12-19
30 Common Terms for Sensors and Photoelectric Sensors — Brief Explanations
As sensors continue to grow in importance, our understanding deepens. Below are 30 common terms and brief explanations related to sensors and photoelectric sensing.
1. Self-diagnosis
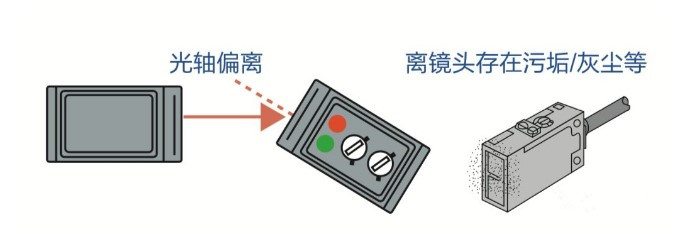
Many modern photoelectric sensors include self-diagnostic outputs. Because dust and oil can interfere with optical sensors, self-diagnosis provides alarms when the sensing lens is contaminated and light levels become unstable.
2. Accuracy: the degree of agreement between a measured result and the true value.
3. Typical sensor structure: sensing element and transducer element.
(1) Sensing element: the part that directly interacts with the measured quantity.
(2) Transducer element: converts the sensing element response into a transmitted or measured electrical signal.
(3) When the output is a standardized signal, the device is called a transmitter.
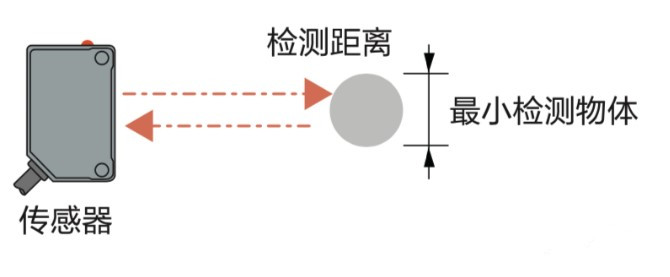
4. Sensing distance: varies by sensor type. For photoelectric sensors:
(1) Through-beam: distance between emitter and receiver.
(2) Retro-reflective: distance between sensor and reflector.
(3) Diffuse-reflective: distance from sensor to object.

5. Repeatability: degree of agreement between successive measurements under the same conditions.
6. Resolution: the smallest change in the measured quantity that the sensor can detect within its range.
7. Threshold: the minimum change in the measured quantity that produces a measurable change at the sensor output.
8. Zero point: the state at which the absolute output value is minimal, for example a balanced state.
9. Linearity: degree to which the calibration curve matches a specified reference.
10. Nonlinearity: degree of deviation of the calibration curve from a specified straight line.
11. Long-term stability: the sensor's ability to remain within allowable error over a specified time.
12. Natural frequency: free oscillation frequency of the sensor when unloaded.
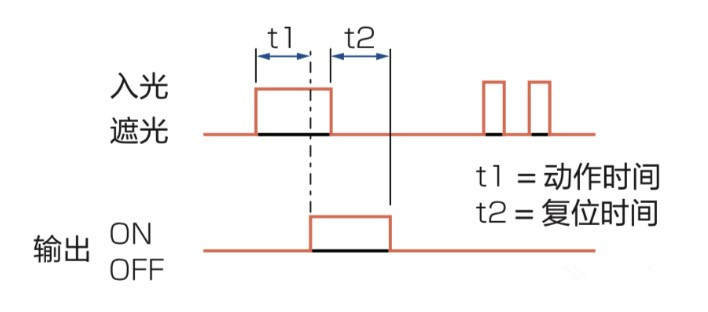
13. Response time
The time required for the sensor to receive input and produce the output signal change.
14. Compensation temperature range: temperature range over which the sensor maintains zero balance and range within specified limits.
15. Creep: change in output over time under constant measured and environmental conditions.
16. Insulation resistance: measured resistance between specified insulated parts under standard temperature.
17. Excitation: external energy (voltage or current) applied for sensor operation.
18. Maximum excitation: highest excitation voltage or current permissible under specified conditions.
19. Input impedance: impedance measured at sensor input when output is shorted.
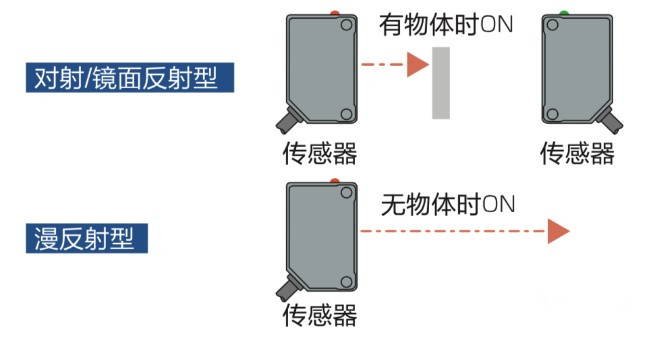
20. Light ON / Dark ON
We commonly use Light ON and Dark ON to select photoelectric modes instead of normally open/closed terminology.
(1) Light ON: receiver outputs ON when sufficient light is received. For through-beam/retro-reflective sensors this is ON with no object; for diffuse sensors it is ON when an object is present.
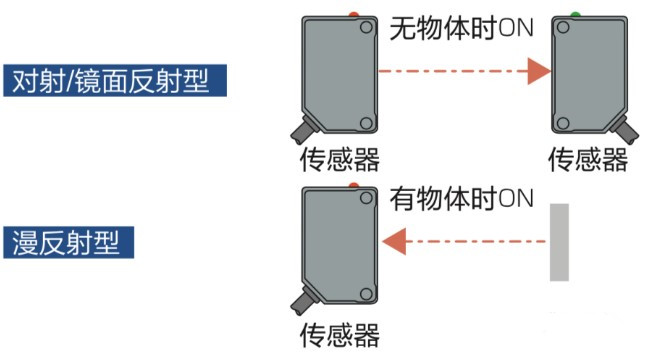
(2) Dark ON: receiver outputs ON when received light is insufficient or absent. For through-beam/retro-reflective sensors this is ON when an object blocks the beam; for diffuse sensors it is ON when no object is present.
21. Output impedance
22. Zero output: sensor output when the measured quantity is zero under specified conditions.
23. Hysteresis: maximum difference in output when the measured value increases versus decreases within a specified range.
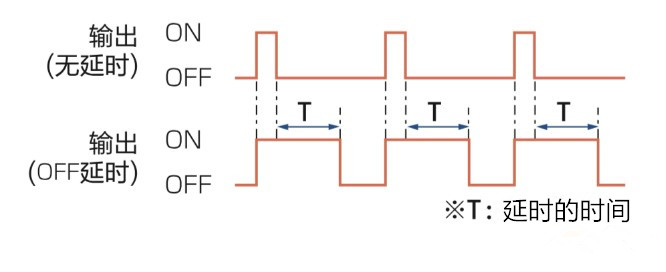
24. Delay: time lag between input change and output change.
25. Drift: undesired change in sensor output unrelated to the measured quantity over time.
26. Zero drift: change in zero output over a specified time and conditions.
27. Sensitivity: ratio of output change to input change.
28. Sensitivity drift: change in calibration slope due to sensitivity variation.
29. Thermal sensitivity drift: sensitivity change caused by temperature.
30. Thermal zero drift: zero-point change due to ambient temperature variation.
These are 30 common sensor and photoelectric sensor terms with brief explanations. We hope this helps.
You May Be Interested
-
Atonm MDSC-9000T Dual-Channel, Single-Sensor Metal Double-Sheet Detector
2025-12-05
-
Non-Contact “One-to-Four” Double-Sheet Detector 1600S: A New Cost-Reduction and Efficiency Solution for Stamping Lines
2025-11-20
-
Mold damage, production delays? Atonm MDSC-8200T metal double-sheet detector protects automotive stamping lines
2025-10-30
-
Provincial Auto Industry Research Tour | Atonm Engages with the Automotive Supply Chain, Empowering Smart Manufacturing through Sensors
2025-10-11





